 |
| Boil, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
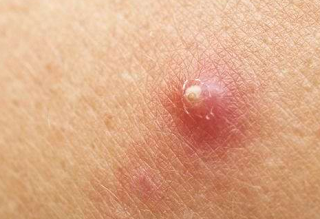
Boils or furuncles are red bumps on the skin that are filled with pus and are painful. This condition is most often caused by a bacterial infection that triggers inflammation of the hair follicle, which is where hair grows.
The body parts most commonly affected by boils are the face, neck, armpits, buttocks, and groin. Boils can also sometimes appear in the pubic area. This happens because these parts often experience friction and sweat. Boils can also grow on the eyelids, which is known as a stye.
Generally, small boils will heal within 2 weeks with proper treatment. However, if the boils that appear get worse and cause other disturbing complaints, treatment needs to be done to prevent the condition from getting worse and complications arise.
Causes of Boils
The main cause of boils is Staphylococcus aureus bacterial infection of the hair follicles. In some people, the bacteria can be found on the skin and in the lining of the nose without causing any problems. New infections will occur if bacteria enter the hair follicles due to scratches or insect bites.
Some of the factors that are thought to increase a person's risk of developing ulcers are:
- Make direct contact with ulcer sufferers, for example because they live at home
- Have a weak immune system, for example because you have HIV, undergoing chemotherapy, or suffering from diabetes
- Having skin problems, such as acne, eczema, or scabies
- Not maintaining cleanliness, both personal and environmental hygiene
- Not meeting the body's nutritional needs properly or suffering from obesity
- Exposure to harmful chemical compounds that can cause skin irritation
In addition to the various causes above, many people think that egg consumption can also cause ulcers. However, this has not been proven true and still needs to be investigated further.
Symptoms of Boils
Boils can appear on any part of the body that is covered with hair or hair, including the ear. However, boils generally grow on body parts that often experience friction and sweating, such as the face, neck, armpits, shoulders, buttocks, groin, and thighs.
Boils can also sometimes appear on the breast. This condition usually occurs in breastfeeding mothers. However, women who are not breastfeeding can also develop breast ulcers.
When you have a boil, a pus-filled lump will appear on the skin, which is characterized by the following signs and symptoms:
- A red bump filled with pus appears which is small at first, but can get bigger
- The skin around the lump will appear red, swollen, and feel warm to the touch
- The lump that appears will be painful, especially when touched
- The bumps have white or yellow dots at the top (pustules) which will then burst and ooze pus
Keep in mind, the bumps that arise when exposed to boils are generally only one. If it arises in large numbers and gathers together, this condition is called a coir ulcer or carbuncle.
A carbuncle indicates a more serious infection. This condition is more often found in middle-aged people who have weak immune systems.
When to go to the doctor
Generally, boils will heal on their own if they are small. However, consult a doctor immediately if the boil gets worse or if:
- Accompanied by fever, unwell, fever, dizziness, or swollen lymph nodes
- Gets worse quickly and is accompanied by severe pain
- Bigger after previous self-medication
- Grows as pimples inside the nose, on the face, ears, or back
- Grows more than one fruit in the same location or forms a carbuncle
- Does not go away after more than 14 days
- Occurs repeatedly (relapses)
- Experienced by people with impaired immune systems
Boil Diagnosis
To diagnose boils, the doctor will ask questions related to the complaints experienced, then proceed with an examination of the skin that has ulcers.
Boils can usually be recognized easily by direct observation. However, if needed, the doctor will take a sample of the patient's pus, skin, or blood, to be examined in a laboratory.
Generally, this follow-up examination will be carried out if:
- Boils that do not heal after treatment or occur repeatedly (relapse)
- Boils arise in large numbers and gather or carbuncle
- Patients who have a weak immune system or suffer from certain diseases, such as diabetes
Bacterial culture tests can also be done to determine which type of antibiotic is suitable for treating boils. This is because the bacteria that cause ulcers often have become resistant to certain types of antibiotics.
Ulcer Treatment
Boils that are small, one in number, and not accompanied by other diseases can usually be treated at home. Some simple ways that can be done to treat boils are:
- Compressing boils with warm water for 10 minutes 4 times a day, to reduce pain while encouraging pus to collect at the top of the lump
- Clean the boil that bursts with sterile gauze and anti-bacterial soap, then cover the boil with sterile gauze
- Change the bandage as often as possible, for example 2-3 times a day
- Wash hands with soap and water before and after treating boils
It's important to remember not to pop the boil on purpose, as this can only exacerbate the infection and spread bacteria, but wait for the boil to burst on its own. If the pain is bothersome, the patient can take pain relievers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
If boils grow in groups and form carbuncles, do not heal after self-treatment, or the patient has a weak immune system, it is advisable to immediately consult a doctor for further treatment.
To treat boils, one of the treatment options that will be carried out is surgery. A surgical procedure is performed to make an incision in the boil and create a channel to drain the pus.
Your doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection, such as erythromycin or clindamycin. Keep in mind, the use of antibiotics must be in accordance with a doctor's prescription. Do not change, reduce, or stop using antibiotics prematurely even if the symptoms have subsided.
Boil Complications
In most cases, boils rarely cause serious complications. However, some complications that can occur due to boils are:
- The appearance of scar tissue
- Recurrent boils (recurrence)
- Spread of infection to deeper layers of the skin (cellulitis)
- Spread of infection into the bloodstream (sepsis)
- Spread of infection to other organs of the body, such as to the heart (endocarditis), bones (osteomyelitis), brain (meningitis), or spinal cord
Boil Prevention
Boils can be prevented by maintaining personal hygiene. Here are some ways that can be applied:
- Shower and wash hands regularly with soap and running water
- Clean and care for the wound properly, if it has a scratch, tear, or cut wound.
- Do not share the use of personal items with others, such as towels, razors, or clothes
- Exercise regularly and eat a healthy diet to boost your immune system
- Avoid direct contact with people with skin infections
Related Searches:
- boils,
- boils on private area pictures,
- seafood boils near me,
- boils on skin,
- what is your body lacking when you get boils,
- what causes boils,
- pictures of boils on private area,
- pictures of boils,
- how to get rid of boils,
- vaginal boils,
- boils on buttocks pictures,
- boils on buttocks,
- boils on inner thigh,
- seafood boils,
- water boils at what temperature,
- antibiotics for boils,
- groin area inner thigh boils,
- home remedies for boils,
- popping huge boils and cysts,
- youtube popping zits and boils,
- boils on body,
- bursting boils and abscesses 2023,
- crab boils near me,
- massive boils bursting,
- pictures of boils on vag lip,
- pizza boils,
- what are boils,
- skin boils,
- boils under armpit,
- home remedies for boils on private area,
- boils on butt,
- are boils contagious,
- drawing salve for boils,
- staph infection boils,
- boils treatment,
- mupirocin ointment for boils,
- mrsa boils,
- home remedies for boils on private area female,
- what do boils look like,
- a watched pot never boils,
- recurring boils on inner thigh,
- gum boils,
- how to prevent boils,
- what causes boils on the skin,
- where do boils come from,
- toothpaste on boils,
- why do i keep getting boils all over my body,
- can stress cause boils,
- temp water boils,
- boils that don't come to a head,
- boils on face,
- how to get rid of vaginal boils,
- why do i keep getting boils,
- boils on private area female,
- boils in groin area female,
- cold water boils faster,
- temperature water boils,
- pictures of gum boils,
- recurring boils,
- boils on the skin,
- popping boils on buttocks,
- how to treat boils,
- water boils at,
- boils on buttocks treatment,
- boils on vagina,
- boils in groin area,
- how do you get boils,
- newest youtube videos infected painful boils,
- black salve for boils,
- best antibiotic for boils,
- boils definition,
- what's in cure for boils,
- how long do boils last,
- prid for boils,
- what causes boils on inner thigh,
- vagina boils,
- hs boils,
- how to get rid of boils on butt,
- ninja blender that boils,
- butt boils,
- scars on buttocks from boils,
- boils on thighs,
- newest youtube videos infected painful boils 2023,
- do boils itch,
- bursting boils and abscesses,
- underarm pimples boils,
- pictures of staph infection boils,
- hidradenitis suppurativa boils,
- popping boils,
- crab boils,
- seafood boils in a bag near me,
- tea tree oil for boils,
- how to treat inner thigh boils,
- ichthammol ointment boils,
- what causes boils on your butt,
- virginia parent boils over,
- ichthammol ointment for boils,
- popping boils videos,
- how to treat boils on inner thighs,
- home remedy for boils,
- furuncles,
- nasal furuncles,
- furuncles and carbuncles,
- furuncles dog paw,
- dog furuncles,
- interdigital furuncles,
- furuncles pictures,
- interdigital furuncles dog,
- carbuncles and furuncles,
- which statement is true regarding coding of carbuncles and furuncles in icd-10-cm?,
- a collection of furuncles,


