 |
| Bronchiectasis, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
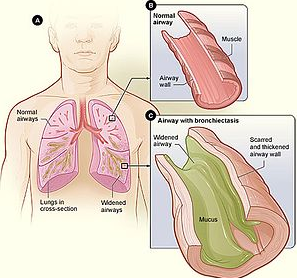
Bronchiectasis is damage and abnormal dilation of the bronchi and respiratory tract. This condition causes a buildup of mucus in the lungs. The most common symptoms of this condition are a persistent cough with phlegm, coughing up blood, and shortness of breath.
The respiratory tract has a protective mechanism to catch dust, bacteria, and dirt from the inhaled air by producing mucus. Under normal conditions, this mucus will be drained out of the respiratory tract and lungs.
In bronchiectasis, the defense function does not work properly so that mucus accumulates in the respiratory tract. Over time, the buildup of mucus can get worse and can lead to a bacterial infection. As a result, damage to the respiratory tract will get worse.
Causes of Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is caused by damage or infection of the walls of the bronchi and respiratory tract. Sometimes, it is not known what caused the damage. However, in the vast majority of cases, bronchial damage is triggered by the following conditions:
- Pneumonia or wet lungs
- TB (tuberculosis)
- Whooping cough
- Cystic fibrosis
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Primary ciliary dyskinesia (abnormality of the fine hairs in the respiratory tract)
- Severe asthma
- Aspiration
- Autoimmune disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Impaired lung development since in the womb
- Connective tissue disorders, such as Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren . syndrome
- Blockage of the respiratory tract, for example due to a tumor
- Weak immune system, for example due to HIV or diabetes
- Measles
Symptoms of Bronchiectasis
Symptoms of bronchiectasis often appear months or years after the patient has had a recurrent respiratory infection. The most common symptoms are:
- Cough with clear, pale yellow, or greenish-yellow phlegm that occurs every day
- Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
- Recurrent respiratory tract infections
- Wheezing or wheezing
- Hard to breathe
- Chest pain
- Muscle ache
- Smelly breath
- Weight loss
- Body feels tired
- Fever and chills
- Sweating at night
- Changes in the shape of the tips of the fingernails (clubbing fingers)
When to go to the doctor
Check with your doctor if you have a persistent cough with phlegm accompanied by the symptoms mentioned above. You are also advised to go to the doctor immediately if the complaint gets worse and shows symptoms such as:
- Bleeding cough
- Cough with phlegm is getting worse, accompanied by greenish phlegm and a bad smell
- Severe chest pain that causes pain when coughing and difficulty breathing
- Body feels very tired
- Lost appetite
- Blue skin and lips
- Breathing too fast
- daze
- Fever
Diagnosis of bronchiectasis
At the beginning of the examination, the doctor will ask the symptoms experienced, for example, how often the patient coughs and whether the cough is accompanied by phlegm. The doctor will also ask which drugs are being consumed and whether there are other diseases that are currently or have been suffered.
Next, the doctor will listen to the sound in the patient's lungs using a stethoscope. Breath sounds produced by the respiratory tract in patients with bronchiectasis are usually abnormal.
In order to determine the cause of bronchiectasis and rule out the possibility of symptoms caused by other diseases, the doctor will perform additional examinations, which include:
- Blood tests, to detect possible infection
- Sputum examination, to determine the presence or absence of bacteria or fungi in the phlegm
- Examination of lung function, to measure the ability of the patient's respiratory tract using spirometry
- Autoimmune screening tests, to determine whether bronchiectasis is caused by an autoimmune disease
- Examination of sweat samples, to determine the possibility of bronchiectasis caused by cystic fibrosis
- X-ray or CT scan of the lungs, to see the condition of the lungs and respiratory tract in detail
- Bronchoscopy, to see if there is blockage or bleeding in the respiratory tract
Bronchiectasis Treatment
Treatment of bronchiectasis aims to relieve symptoms, address the underlying cause, and prevent complications. The sooner treatment is given, the greater the patient's chance of avoiding further lung damage.
The types of treatment used to treat bronchiectasis include medication, therapy, and surgery, as described below:
Drugs
The doctor will prescribe a number of drugs to treat the infection and reduce symptoms, such as:
- Antibiotics, which are available in the form of oral or inhaled drugs
- Bronchodilators, such as beta 2-adrenergic agonists, anticholinergics, and theophylline
- Expectorants (phlegm thinners), which can be used alone or in combination with decongestants
Therapy
A number of therapies that patients can undergo to relieve symptoms of bronchiectasis are:
- Use of a special vest
- Chest clapping therapy
- Use of breathing apparatus (positive expiratory pressure)
- Breathing therapy called the active cycle of breathing technique (ACBT)
In addition to the methods above, people with bronchiectasis are encouraged to take the following measures to help relieve symptoms:
- Quit smoking
- Exercise regularly
- Wash your hands regularly
- Drink lots of water to stay hydrated
- Eat a balanced nutritious diet
- Get a flu shot every year
- Get the pneumonia vaccine to prevent pneumonia
Operation
The doctor will suggest surgery if the bronchiectasis only affects one lobe (section) of the lung, or if the patient's condition does not improve after medication or therapy is given. The operation is performed by removing the affected lobe of the bronchiectasis.
Please note that the above treatment methods only prevent bronchiectasis from getting worse. This is because lung damage from bronchiectasis is permanent and difficult to heal.
Complications of Bronchiectasis
Severe bronchiectasis can progress to a more serious condition and require emergency treatment. These serious conditions include:
- Coughing up large amounts of blood
- Atelectasis
- Lung abscess
- Breathing failure
- Heart failure
Prevention of Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis caused by birth defects is a condition that cannot be prevented. However, bronchiectasis that occurs due to respiratory tract infections can be prevented by avoiding the triggering factors, namely by taking the following steps:
- Avoid air pollution, including factory fumes and vehicle fumes
- Do not smoke and avoid exposure to cigarette smoke
- Get vaccinated to prevent whooping cough, tuberculosis, pneumonia, measles, and COVID-19
- Keep the child from inhaling objects that can clog the respiratory tract
- Undergo treatment and regular check-ups if bronchiectasis is diagnosed early, so that the disease does not get worse
Related Searches:
- bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis definition,
- bronchiectasis treatment,
- bronchiectasis symptoms,
- bronchiectasis icd 10,
- what is bronchiectasis,
- traction bronchiectasis,
- icd 10 code for bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis vs bronchitis,
- icd 10 bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis x ray,
- bronchiectasis medical definition,
- bronchiectasis causes,
- bronchiectasis pronunciation,
- copd bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis copd,
- is bronchiectasis copd,
- bronchiectasis and coffee,
- define bronchiectasis,
- retraction bronchiectasis,
- types of bronchiectasis,
- cylindrical bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis types,
- new treatments for bronchiectasis,
- cystic bronchiectasis,
- what causes bronchiectasis,
- what is the most common cause of bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis cxr,
- mild bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis and covid-19,
- bronchiectasis cystic fibrosis,
- cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis diagnosis,
- bronchiectasis vs copd,
- bronchiectasis life expectancy,
- bronchiectasis signs and symptoms,
- copd vs bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis chest x ray,
- life expectancy with bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis vs chronic bronchitis,
- is bronchiectasis a terminal illness,
- chronic bronchitis vs bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis is,
- icd 10 for bronchiectasis,
- non cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis exacerbation,
- bronchiectasis complications,
- bronchitis vs bronchiectasis,
- new treatments for bronchiectasis 2023,
- bronchiectasis foods to avoid,
- bronchiectasis mayo clinic,
- pathophysiology of bronchiectasis,
- causes of bronchiectasis,
- chronic bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis meaning,
- bronchiectasis pathophysiology,
- bronchiectasis.,
- emphysema vs bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis cure,
- non cf bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis prognosis,
- how serious is bronchiectasis,
- bronchiectasis airway clearance technique,
- bronchiectasis vs emphysema,


