Chickenpox, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications
 |
| Chickenpox, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
Definition of Chicken Pox
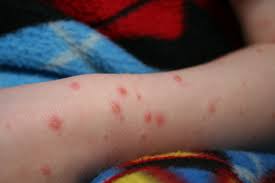
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the Varicella zoster virus. This disease is characterized by symptoms in the form of a red rash filled with fluid that feels very itchy all over the body.
Chickenpox was once a common disease in children. However, after the chickenpox vaccination was carried out since the 1990s, the cases of chickenpox began to decrease gradually.
Chickenpox can cause serious complications in infants, pregnant women, and people with weak immune systems, such as people with HIV/AIDS.
Symptoms and Causes of Chicken Pox
The symptom of chickenpox is a red rash on the face, chest, or back, which can spread to all parts of the body. Chickenpox is also characterized by other complaints, such as:
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Chickenpox in medical terms is known as varicella. The cause is a virus that is easily transmitted through saliva splashes, or direct contact with fluids that come from the rash.
This disease is more susceptible to attack children under the age of 12 years. Some other factors that can increase the risk of chickenpox are not having had chickenpox before and not receiving the chickenpox vaccine.
Chickenpox Treatment and Prevention
Chickenpox treatment aims to reduce the severity of symptoms, with or without medication. There are several efforts that can be done to relieve symptoms, namely wearing loose clothing and soft materials, and not scratching the rash or chickenpox sores.
Prevention of chickenpox is to get the chickenpox vaccine or varicella vaccine. In Indonesia, the chickenpox vaccine is not included in the complete routine immunization list, but it is still recommended to be given.
Causes of Chicken Pox
Chickenpox is caused by the Varicella zoster virus. Varicella is a herpes virus that is categorized into a group of infectious organisms such as genital herpes.
This virus can be transmitted very easily and quickly through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, as well as direct contact with mucus, saliva, or fluids from a rash. This infection can occur 1–2 days before the rash appears and will remain contagious until the entire rash has dried.
Newborns of mothers who have not been vaccinated against smallpox are at risk of developing this disease. The risk of chickenpox is also higher in people with the following conditions:
- Never had chickenpox
- Haven't received the chickenpox vaccine yet
- Have a weak immune system, for example due to suffering from HIV/AIDS, cancer, using corticosteroid drugs, or undergoing chemotherapy
- Working in a public facility, such as a school or hospital
- Under 12 years old
Symptoms of Chicken Pox
The symptom of chickenpox is a blistering rash that appears 10–21 days after exposure to the Varicella virus. The rash usually appears first on the chest, back, or face, then spreads to the rest of the body. In fact, the rash can sometimes spread to the mouth, eyelids, and genital area.
Symptoms of a rash in chickenpox can also be accompanied by other complaints, such as:
- Fever with a temperature of 38.3–38.8°C
- Sore throat
- Mild stomach ache
- Headache
- Tiredness and weakness (malaise)
- Loss of appetite
When to go to the doctor
Chickenpox generally does not require special treatment, because it can heal on its own. However, it is still necessary to see a doctor if you or your child has a rash and other symptoms of chickenpox.
In addition, be aware if certain symptoms of chickenpox appear, such as:
- Fever more than 4 days
- Severe cough and shortness of breath
- The rash becomes very red, swollen, painful to the touch, feels warm, and oozes pus
- Difficulty eating and drinking, causing dehydration
- Severe headache
- Often sleepy and difficult to wake up
- The rash spreads to one or both eyes
- Vomiting constantly
- Looks dazed
- Stiff neck
Chickenpox Diagnosis
In most cases, doctors can diagnose chickenpox by looking at the characteristics of the rash on the patient's body. However, the doctor will also ask if there are other symptoms that accompany the rash.
To further confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may also perform additional examinations, such as:
- blood test
- The doctor will take a sample of the patient's blood to be examined in the laboratory. The goal is to confirm the presence of a viral infection.
- Virus culture
- Virus culture is done by taking a sample of fluid from the rash on the patient's body. The fluid sample will then be examined in the laboratory to detect the presence of the Varicella virus.
Chickenpox Treatment
The method of treating chickenpox will be adjusted to the symptoms experienced by the patient, including:
Drug Administration
Your doctor may prescribe an ointment or oral antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine, to relieve itching. However, please note, chickenpox drugs available in pharmacies can cause certain side effects. Therefore, the doctor may also prescribe a new generation of antihistamine drugs, such as:
- Loratadine
- Cetirizine
- Fexofenade
Meanwhile, to relieve other symptoms, such as headache, fever, fatigue, or muscle aches, the doctor will prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as paracetamol. However, consult your doctor first before using over-the-counter pain relievers.
It is important to remember, giving aspirin to people with chickenpox is not recommended, because it can cause Reye's syndrome. Other NSAIDs, namely ibuprofen, are also not recommended to be used, because they can trigger secondary infection or tissue damage.
Keep in mind, the habit of scratching the chickenpox rash can cause a bacterial infection. If the patient has a secondary bacterial infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
Meanwhile, for people with chickenpox who are at risk for complications, the doctor will give antiviral drugs, such as:
- Valacyclovir
- Acyclovir
- Famciclovir
Although it cannot cure chickenpox, the drugs for chickenpox above can inhibit the activity of the virus so that the symptoms that appear are lighter. That way, the patient's immune system can recover faster.
Self Care
Chickenpox that occurs in patients with weak immune systems does not require special treatment. However, there are some independent efforts that can be made to help relieve symptoms. Some of these efforts are:
- Drink plenty of fluids and eat foods that are soft and not salty or sour, especially if you have a smallpox rash in your mouth.
- Avoid scratching chickenpox rashes or sores, as they increase the risk of infection. To prevent this, cut your nails short or wear gloves, especially at night.
- Wear clothes made of soft and light.
- Take a warm bath 3-4 times a day, for a few days after the rash appears. After that, dry by patting with a towel until dry.
- Use calamine lotion on the itchy area.
- Compress the rash or wound with cold water to relieve itching.
- Get enough rest and avoid contact with other people to prevent the spread of chickenpox.
Chickenpox Complications
After recovering from chickenpox, the Varicella zoster virus will remain in the nerve cells. The virus can be reactivated several years later in the form of shingles (herpes zoster).
The appearance of smallpox can be experienced by adults who have been exposed to chickenpox, especially those who have low immune systems.
Complications of chickenpox are susceptible to newborns, pregnant women, adults who have never had chickenpox, and people with weak immune systems. Some of these complications include:
- Secondary bacterial infections that attack the skin, soft tissues, bones, and joints in children
- Blood stream infection (sepsis)
- Lung infections (pneumonia), especially in smokers
- Infection or inflammation of the brain (encephalitis)
- Pockmarks or scar tissue
- Dehydration
- Dead
In addition, chickenpox infection during pregnancy is at risk of causing complications to the fetus, such as:
- Low birth weight
- Growth disorders
- Small head size
- Visual disturbance
- Intelligence disorder
Chickenpox that occurs a week before delivery or a few days after the baby is born, is at risk of causing serious infections that can be life-threatening.
Chickenpox Prevention
An effective way to prevent chickenpox is to undergo the chickenpox vaccination. This vaccination is recommended for children and adults who have not received the chickenpox vaccine.
In young children, the first chickenpox vaccination is carried out at the age of 12-15 months, and the follow-up vaccine is given when the child is 4-6 years old. As for adolescents and adults, the chickenpox vaccine is given in two doses with a time difference of at least 28 days.
Meanwhile, in people who have had chickenpox, vaccination is not necessary. This is because after recovering, his body will form antibodies against the Varicella virus so it is less likely to get chickenpox again. Even if infected again, the symptoms that appear will be lighter.
Please note, chickenpox vaccination is not recommended for pregnant women, people with weak immune systems, and people who are allergic to gelatin or neomycin. In these conditions, avoid contact with people with chickenpox to prevent transmission of the virus.
If a family member has chickenpox, there are several things you can do to prevent transmission of the infection, namely:
- Separate the patient in another room.
- Avoid contact with sufferers, because the virus can spread through the air.
- Wash hands with soap and running water after each contact with an infected person.
- Avoid sharing eating utensils with sufferers.
- Always clean and disinfect furniture surfaces in the home area.
- Remind family members who are infected with chickenpox not to scratch the rash, because the fluid in the rash is easily contagious.
- Cut the patient's nails or ask him to wear cotton gloves, to reduce the risk of skin damage from scratching.
- Instruct the patient to stay at home until all rashes are dry.
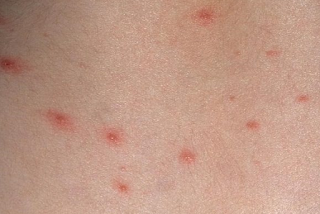
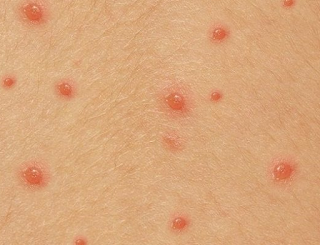
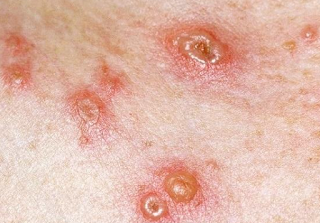
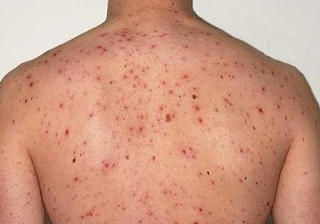
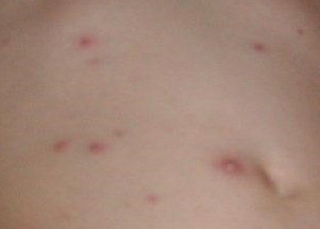
Chicken Pox Pictures
The chickenpox rash usually lasts for about 5–10 days. This rash has three stages of development before then disappearing. These stages are:
1. Red rash spots appear on the skin.
2. The rash becomes like blisters filled with fluid (vesicles), which can burst within a few days.
3. The blisters that burst will then take some time to eventually turn into dry crusts.
The three stages of chickenpox rash development do not occur at the same time. New rashes will appear continuously as long as the infection is still there, and only subside until it disappears completely within 14 days.
Chickenpox in Adults
Although it affects more children, adults are still at risk of contracting chickenpox. In fact, the symptoms of chickenpox in adults can be more severe than those of chickenpox in children.
Chickenpox in adults
Even so, it is unlikely for adults to have repeated chickenpox. This is because the body's immunity to the virus that causes chickenpox is active after the patient recovers.
Comparison Between People Who Have Received Vaccines and Those Who Have Not Received Vaccines
Vaccines work by helping to protect the body's immune system and prevent certain viruses from attacking. People who have received the Varicella vaccine generally will not get chickenpox. Even if you get chickenpox, usually only milder symptoms will occur, or even no symptoms at all.
People with chickenpox who have received the vaccine.
People with chickenpox who do not get the vaccine.
Related Searches:
- chickenpox,
- chickenpox vaccine,
- chickenpox symptoms,
- can you get shingles if you never had chickenpox,
- when did the chickenpox vaccine come out,
- what do chickenpox look like,
- chickenpox vaccine age,
- can you get shingles if you had chickenpox,
- chickenpox in adults,
- monkeypox vs chickenpox,
- smallpox vs chickenpox,
- how does chickenpox spread,
- what causes chickenpox,
- chickenpox in spanish,
- how is chickenpox spread,
- chickenpox and shingles,
- is there a vaccine for chickenpox,
- chickenpox vaccine history,
- shingles vs chickenpox,
- chickenpox treatments,
- signs of chickenpox,
- how do you get chickenpox,
- how long is chickenpox contagious,
- adult chickenpox,
- chickenpox vaccine for adults,
- shingles and chickenpox,
- is chickenpox herpes,
- pictures of chickenpox,
- can i get shingles if i never had chickenpox,
- treatment for chickenpox,
- how long does chickenpox last,
- when was the chickenpox vaccine created,
- when do kids get chickenpox vaccine,
- chickenpox treatment,
- how does chickenpox start,
- chickenpox vs shingles,
- is chickenpox still around,
- chickenpox smallpox,
- symptoms of chickenpox,
- chickenpox vs hand foot mouth,
- chickenpox vaccine efficacy,
- how long did it take to develop the chickenpox vaccine,
- chickenpox shingles,
- can you get shingles if you had the chickenpox vaccine,
- dangers of chickenpox vaccine,
- is chickenpox airborne,
- is there a chickenpox vaccine,
- chickenpox transmission,
- efficacy of chickenpox vaccine,
- chickenpox after vaccine,
- how contagious is chickenpox,
- chickenpox vaccine schedule,
- chickenpox airborne,
- chickenpox in adults second time,
- chickenpox vs smallpox,
- symptoms of chickenpox in adults,
- does the chickenpox vaccine prevent shingles,
- can you die from chickenpox,
- images of chickenpox,
- can you get chickenpox twice,
- when do babies get chickenpox vaccine,
- can chickenpox kill you,
- when was the chickenpox vaccine invented,
- chickenpox vaccine side effects how long after,
- hives vs chickenpox,
- how long does the chickenpox vaccine last,
- chickenpox vs hives,
- chickenpox in adults pictures,
- can you get shingles if you ve had chickenpox,
- cdc chickenpox,
- how do you catch chickenpox,
- what is chickenpox,
- chickenpox vaccine side effects cdc,
- where did chickenpox come from,
- chickenpox symptoms in adults,
- is one dose of chickenpox vaccine enough,
- does chickenpox vaccine prevent shingles,
- early signs of chickenpox,
- how do chickenpox start,
- chickenpox in mouth,
- rash after chickenpox vaccine picture,
- treatment of chickenpox,
- mild case of chickenpox,
- chickenpox vaccine side effects,
- can you get chickenpox from shingles,
- where do chickenpox start,
- beginning of chickenpox,
- is chickenpox deadly,
- show me a picture of chickenpox,
- chickenpox scars,
- chickenpox vaccine effectiveness,
- breakthrough chickenpox,
- what chickenpox look like,
- delta variant chickenpox,
- chickenpox virus,
- how do chickenpox look,
- chickenpox rash,
- chickenpox vaccine scar,
- difference between smallpox and chickenpox,
- difference between chickenpox and smallpox,


Post a Comment for "Chickenpox, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications"