 |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
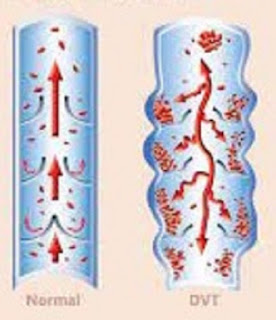
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or deep vein thrombosis is a blood clot in one or more deep veins. In most cases, DVT forms in the veins of the thigh or calf, but it can occur in the veins of other parts of the body.
A blood clot or clot is blood that changes from a liquid form to a rather solid gel through a process called coagulation. When a cut or injury occurs, the blood will clot to make the bleeding stop.
In deep vein thrombosis, there is a blood clot in the deep vein that blocks blood flow. If left unchecked, these blood clots can dislodge and follow the bloodstream, then clog arteries in the lungs. As a result, the patient will have difficulty breathing, even death.
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is caused by a disease or condition that prevents blood from flowing or clotting normally. There are three factors that can cause this, namely:
- Damage to the veins
- Impaired blood flow in the veins
- Conditions that make blood clot more easily (hypercoagulability)
Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis
Various diseases or conditions that cause the three factors above can increase the risk of DVT. In other words, a person is more at risk of developing deep vein thrombosis if they have the following conditions or diseases:
- Over 60 years old
- Have a smoking habit
- Using injectable drugs
- Taking chemotherapy drugs
- Have a genetic disorder that causes the blood to clot more easily, such as Factor V Leiden, nephrotic syndrome, and antiphospholipid syndrome
- Taking long trips by car, train, or plane, which keeps your feet from moving much
- Undergoing bed rest, being paralyzed, or suffering from an illness that keeps the legs from moving for a long time
- Suffering from a heart attack, heart failure, cancer, colitis, being overweight, or obese
- Have a history of surgery on veins, such as heart surgery, abdominal surgery, or knee and hip replacement surgery
- Have a history of lower body injuries, such as fractures of the femur, leg, or pelvis
- Suffering from diseases that interfere with the function of blood vessels, such as vasculitis and varicose veins
- Experiencing increased levels of the hormone estrogen, for example due to pregnancy, recently giving birth, and taking birth control pills or estrogen replacement drugs
- Have a history of DVT or pulmonary embolism, either in yourself or in the family
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
In some cases, DVT has no symptoms at all. However, some of the complaints that usually arise due to DVT can include:
- The limbs with DVT feel warm
- Pain that gets worse when bending the leg
- Swelling in one leg, especially in the calf
- Cramps that usually start in the calves, especially at night
- Changes in the color of the legs to pale, red, or darker
When to go to the doctor
Immediately see a doctor if you experience the symptoms of DVT mentioned above. If not treated immediately, a DVT blood clot can travel to the lungs and cause the blood vessels in the lungs to become blocked. This condition is known as a pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary embolism is a medical emergency that must be watched out for, with symptoms such as:
- Bleeding cough
- The pulse is fast
- Shortness of breath or sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain that gets worse when you cough or take a deep breath
- Dizziness and feeling like passing out
Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosis
To diagnose deep vein thrombosis, the doctor will ask about the patient's symptoms and medical history. Next, the doctor will perform a physical examination of the sore and swollen body part.
After that, the doctor will perform a series of supporting examinations, such as:
- blood test
- Doppler ultrasound
- Venography
- MRI
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment
DVT treatment aims to prevent blood clots from getting bigger, prevent pulmonary embolism, and reduce the risk of DVT recurrence. Treatment methods include:
1. Drugs
The drugs given to patients with DVT are anticoagulant drugs, such as heparin and warfarin. This drug works to prevent blood clots from growing and reduce the risk of new blood clots forming.
If the patient's DVT is severe enough or there is a pulmonary embolism, the doctor will prescribe thrombolytic drugs. This drug works by breaking up blood clots quickly.
2. Filter the vena cava
If medication is not effective, the doctor will place a special filter in the main abdominal cavity blood vessel (vena cava). The filter serves to prevent blood clots from entering the lungs and causing pulmonary embolism.
However, keep in mind that installing filters in the long term can actually make the condition worse. Therefore, the filter should be removed after the risk of complications is reduced.
3. Compression stockings
Compression stockings are worn below or above the knee to prevent swelling from DVT. Doctors will advise patients to wear these compression stockings every day, for at least 2 years. The goal is to reduce the risk of new blood clots forming.
4. Thrombectomy
Thrombectomy is performed if the blood clot is large and causes tissue damage. This procedure is done by making small incisions in the blood vessels. After that, the doctor will remove the blood clot, then repair the damaged tissue and blood vessels.
In some cases, the doctor will use a special balloon to keep the blood vessels wide open during the process of removing the blood clot. After that, the balloon will be lifted along with the blood clot.
Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis can cause serious complications, including:
- Pulmonary embolism, which is blockage of arteries in the lungs due to blood clots that escape from the legs
- Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), which is impaired blood flow in the veins due to DVT
Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis caused by genetic disorders cannot be prevented. However, to prevent DVT due to other conditions or diseases, there are several efforts that can be done, namely:
- If you've recently been on bed rest for a long time, move your legs occasionally or walk if you can to keep blood flowing.
- If you're on a long commute or your job requires you to sit for long periods of time, do some simple leg movements or get up from your seat occasionally to walk.
- If you have recently had surgery, take anticoagulants prescribed by your doctor to reduce the risk of blood clots forming after surgery.
- Live a healthy lifestyle, such as not smoking, eating a balanced nutritious diet, maintaining an ideal body weight, and exercising regularly.
Related Searches:
- deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis symptoms,
- deep vein thrombosis treatment,
- deep vein thrombosis pictures,
- what is deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis treatments,
- treatment deep vein thrombosis,
- what causes deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis medication,
- deep vein thrombosis icd 10,
- treatment for deep vein thrombosis,
- symptoms of deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis causes,
- signs of deep vein thrombosis,
- chronic deep vein thrombosis icd 10,
- what are the warning signs of deep vein thrombosis?,
- deep vein thrombosis in leg,
- what does deep vein thrombosis feel like,
- what does a deep vein thrombosis feel like,
- compression stockings for deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis icd 10 code,
- deep vein thrombosis treatment at home,
- deep vein thrombosis leg,
- deep vein thrombosis behind knee,
- deep vein thrombosis diagnosis,
- deep vein thrombosis compression stockings,
- deep vein thrombosis test,
- deep vein thrombosis in arm,
- dvt deep vein thrombosis,
- diagnosing deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis how to diagnose,
- deep vein thrombosis leg pictures,
- icd 10 code for deep vein thrombosis,
- diagnose deep vein thrombosis,
- how is deep vein thrombosis diagnosed,
- diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis dvt,
- deep vein thrombosis in leg pictures,
- preventing deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis prevention,
- deep vein thrombosis definition,
- prevent deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy,
- medication for deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis pregnancy,
- prevention of deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis thigh,
- deep vein thrombosis in thigh,
- deep vein thrombosis medications,
- what are the symptoms of deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis risk factor,
- deep vein thrombosis risk factors,
- risk factors for deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis medical devices,
- peroneal vein deep vein thrombosis,
- icd 10 deep vein thrombosis unspecified,
- what is deep vein thrombosis symptoms,
- leg deep vein thrombosis pictures,
- deep vein thrombosis in foot,
- deep vein thrombosis foot,
- how to treat deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis how to treat,
- what are the warning signs of deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis calf,
- deep vein thrombosis on foot,
- how is deep vein thrombosis treated,
- acute deep vein thrombosis icd 10,
- deep vein thrombosis signs and symptoms,
- what does deep vein thrombosis look like,
- icd 10 deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis cartoon,
- pathophysiology of deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis treatment walking,
- what does a deep vein thrombosis look like,
- images of deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis signs,
- symptoms of deep vein thrombosis in leg,
- deep vein thrombosis image,
- pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis complications,
- deep vein thrombosis symptoms leg,
- specialist for deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism,
- deep vein thrombosis leg symptoms,
- signs and symptoms of deep vein thrombosis,
- acute deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis arm,
- yaz deep vein thrombosis,
- how to prevent deep vein thrombosis,
- bilateral deep vein thrombosis icd 10,
- deep vein thrombosis specialists,
- deep vein thrombosis (dvt),
- varicose veins vs deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis in ankle,
- deep vein thrombosis pictures calf,
- deep vein thrombosis surgery,
- pictures of deep vein thrombosis in calf,
- what is a deep vein thrombosis,
- deep vein thrombosis in spanish,
- causes of deep vein thrombosis,


