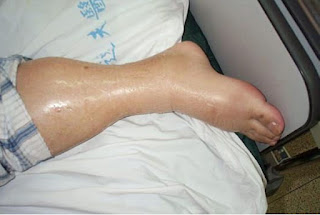
Edema is a buildup of fluid in body tissues. Edema most often occurs in the legs or arms. However, this condition can also occur in other parts of the body, such as the stomach and face
 |
| Edema, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
Edema in mild cases is common and usually harmless. However, edema can also be a sign of serious illness, such as heart failure, as well as disorders of the liver, kidneys or brain. Therefore, it is very important to see a doctor when edema occurs to find out the underlying cause.
Causes of Edema
Edema occurs when fluid in the blood vessels escapes into the surrounding tissue. The fluid then accumulates and makes body tissue swollen.
Edema in mild cases can result from:
- Standing or sitting for too long
- Excessive consumption of foods with high salt content
- Hormonal changes during premenstrual period
- Pregnancy, because the body retains more salt and water than usual
Apart from the conditions above, edema can also occur due to serious conditions, namely:
1. Deficiency of protein albumin
Proteins, including albumin, play a role in keeping fluid in the blood vessels. Lack of protein in the blood can cause fluid in the blood vessels to escape and accumulate, causing edema.
Conditions that can cause albumin deficiency include malnutrition and cirrhosis.
2. Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions, for example due to insect bites or animal dander, can cause edema. This happens because the body's response to the allergen causes fluid in the blood vessels to flow into the area.
3. Damage to the veins in the legs
This condition occurs in chronic venous insufficiency disease. This disease causes interference with the veins in the legs. As a result, fluid in the bloodstream accumulates in the blood vessels and leaks out into the surrounding tissues.
4. Heart failure
When the heart begins to fail, one or both chambers of the heart lose their ability to pump blood effectively. As a result, fluid will slowly accumulate and cause edema in the legs, lungs or stomach.
5. Kidney disease
Edema may result from kidney disease, particularly nephrotic syndrome and chronic renal failure. This happens because fluids in the body cannot be excreted through damaged kidneys, causing accumulation. Edema caused by kidney disease, can occur in the legs or the area around the eyes.
6. Burns
Severe burns can also cause edema. This is because burns can cause fluid to leak into tissues throughout the body.
7. Infection
As with burns, severe infections, such as cellulitis or COVID-19, can also cause fluid to leak into the tissues of the infected body part.
8. Disorders of the lymph flow system
The lymphatic system functions to clear excess fluid from the tissues. Damage to this system can cause the lymph nodes in an area of the body to not function properly resulting in a buildup of fluid.
9. Drug side effects
Several types of drugs can cause side effects in the form of edema. Examples are antihypertensive drugs, corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), estrogen hormones, and diabetes drugs.
Apart from the causes above, edema can also occur due to disorders of the brain, such as head injuries, brain tumors, brain infections, and fluid blockages in the brain. Edema caused by disorders of the brain only cause edema in the brain.
Oedema risk factors
There are a number of factors that can increase the risk of developing edema, namely:
- Female gender
- Old age (elderly)
- Having excess body weight
- Taking certain medications, such as antihypertensive drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or diabetes medications
- Suffer from chronic diseases, such as heart failure and kidney disease
- Just had surgery
Edema symptoms
Symptoms that can arise due to edema depend on the condition and location of the swollen tissue. Complaints that appear and can be felt by sufferers are:
- Swelling of the affected limb, such as an arm or leg
- The skin in the area affected by edema becomes tight and shiny
- A hole like a dimple appears for a few seconds if the skin on the area of edema is pressed
- Enlarged belly size
- Shortness of breath and cough if there is edema in the lungs
- It is difficult to walk because the legs feel heavier due to swelling
Apart from the complaints above, other symptoms can also appear due to edema caused by inflammation. Some of the symptoms are fever, as well as skin redness, pain, or limited movement in the part that has edema.
When to see a doctor
Check with your doctor if you experience the symptoms mentioned above, especially if the symptoms appear after doing activities that make you sit or stand for a long time, such as taking a long trip.
In addition, you need to see a doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of edema, such as:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain
- Cough
The above symptoms can be a sign of pulmonary edema and can be fatal if not treated immediately.
You are also advised to see a doctor immediately if your stomach is enlarged, you have severe leg edema that makes it difficult to walk, or you have edema throughout your body (anasarka edema).
Edema diagnosis
To diagnose edema, the doctor will conduct a question and answer regarding the complaints experienced, medical history, and drugs consumed by the patient.
After that, the doctor will carry out a physical examination of the area that is experiencing swelling, followed by examining the condition of the liver, kidneys and heart.
Doctors can also carry out supporting examinations to determine the cause of edema, including:
- Blood tests, to check kidney function, liver and albumin levels
- Urine test, to check for protein and blood levels in the urine
- Scanning with X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, to detect the underlying cause of edema, such as damage to the veins
- Echocardiography, to detect whether edema is related to heart problems, such as heart failure
Edema Treatment
In mild cases, the edema will heal on its own with rest. However, in severe cases, the doctor will give medicines whose types are adjusted to the cause, such as:
- Antiallergic drugs, to treat edema caused by allergic reactions
- Blood thinners, to treat edema due to damage to blood vessels
- Diuretic drugs, to treat edema associated with heart failure or liver disease
In edema that occurs due to drug side effects, the doctor can adjust the type and dosage of the drug so as not to cause edema in the patient.
In addition to the treatment methods above, there are several efforts that can be made to relieve symptoms and help the healing process, namely:
- Do not smoke
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Reducing consumption of alcoholic beverages
- Don't sit or stand for too long
- Propping your feet while lying down
- Get regular exercise, such as walking or swimming
- Reducing salt intake in food
- Using special stockings to prevent the feet from getting swollen
Edema complications
If left untreated, edema can cause the following complications:
- Hard to walk
- Pain that gets worse
- Rigid
- The skin stretches causing itching, discomfort, and open sores
- Infection in the part that is experiencing swelling
- Scars between layers of tissue
- Decreased elasticity of blood vessels, joints and muscles
Edema Prevention
Prevention of edema depends on the cause. Generally, edema can be prevented by living a healthy lifestyle, such as:
- Exercise regularly
- Eat foods with complete and balanced nutrition
- Limit salt consumption
- Maintain body weight to remain ideal
Apart from doing the things above, it is also recommended that you carry out regular check-ups if you suffer from diseases that can cause edema, such as diabetes, heart failure or kidney disease.
Related Searches:
- pulmonary edema,
- pitting edema,
- what is edema,
- edema definition,
- peripheral edema,
- cerebral edema,
- periorbital edema,
- edema in legs,
- pitting edema scale,
- macular edema,
- pedal edema,
- flash pulmonary edema,
- edema treatment,
- corneal edema,
- heat edema,
- what causes edema,
- dependent edema,
- bone marrow edema,
- edema icd 10,
- how to treat edema,
- edema medical term,
- edema meaning,
- edema ankles,
- non pitting edema,
- edema scale,
- vasogenic edema,
- edema in feet,
- pulmonary edema treatment,
- weeping edema,
- what is pulmonary edema,
- define edema,
- marrow edema,
- how to drain edema fluid,
- edema face,
- brain edema,
- cystoid macular edema,
- pulmonary edema icd 10,
- icd 10 code for edema,
- lower extremity edema,
- acute pulmonary edema,
- pitting edema causes,
- scrotal edema,
- angioneurotic edema,
- diabetic macular edema,
- anasarca edema,
- icd 10 edema,
- leg edema,
- reinke's edema,
- lower extremity edema icd 10,
- what causes edema in legs,
- pretibial edema,
- laryngeal edema,
- icd 10 code for pulmonary edema,
- pulmonary edema symptoms,
- can edema kill you,
- facial edema,
- edema causes,
- interstitial edema,
- peripheral edema icd 10,
- eyelid edema,
- edema grading,
- brawny edema,
- scleral edema,
- types of edema,
- causes of edema,
- pulmonary edema vs pleural effusion,
- pitting vs non pitting edema,
- what is pitting edema,
- foot edema,
- diuretics for edema,
- heart failure edema,
- symptoms of edema,
- pulmonary edema cxr,
- sacral edema,
- pitting edema in legs,
- edema symptoms,
- generalized edema,
- localized edema,
- edema medical definition,
- high altitude cerebral edema,
- subcutaneous edema,
- oedema vs edema,
- pulmonary edema x ray,
- edema pulmonar,
- cardiogenic pulmonary edema,
- edema legs,
- bilateral lower extremity edema icd 10,
- leg edema icd 10,
- icd 10 code for peripheral edema,
- myocardial edema,
- bone edema,
- how to get rid of edema,
- edema in eyes,
- soft tissue edema,
- edema blister,
- periportal edema,
- causes of edema in legs,
- best otc diuretic for edema,
- cytotoxic edema,


