Epididymitis, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications
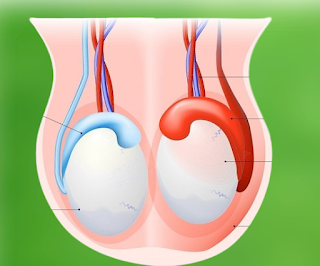
Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis which is generally caused by a bacterial infection. This condition can be characterized by swelling of the testicles. Epididymitis can be experienced by men of any age, but is most common in the 19–35 year age group.
 |
| Epididymitis, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
The epididymis is the tube that connects the testes to the vas deferens, which is the tube that carries sperm to the penis. The function of the epididymis is as a place for sperm maturation. In addition, the epididymis can also contract to push sperm out during ejaculation.
When epididymitis occurs, inflammation causes swelling and pain in the epididymis. This condition will usually improve with antibiotics. However, if treated too late, inflammation can spread to the testicles (epididymo-orchitis).
Causes of Epididymitis
Epididymitis can be caused by infectious or non-infectious diseases. The following is an explanation:
Infectious disease
Types of infectious diseases that cause epididymitis include:
- Sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea
- Viral infections, such as the mumps virus
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacterial infection
- Cryptococcus and cytomegalovirus infections that occur in patients with weak immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients
Non-infectious disease
Although generally caused by infection, epididymitis can also be caused by non-infectious diseases, such as:
- Prostate enlargement
- Urinary reflux, which is a condition when urine flows into the epididymis which generally occurs as a result of overstretching the body or lifting heavy objects
- Testicular torsion
- Injury in the groin area
- Autoimmune diseases, such as sarcoidosis or Behçet's disease
- Complications of surgery on the genitals, such as vasectomy
- Long-term use of urinary catheters
- Amiodarone side effects
Epididymitis Risk Factors
There are a number of factors that can increase a person's risk of developing epididymitis, namely:
- Have had a sexually transmitted infection, prostate inflammation (prostatitis), or urinary tract infection
- Have had medical procedures on the urinary tract, prostate, or bladder
- Suffering from urinary tract deformities
- Not undergoing circumcision
Epididymitis symptoms
The following are some of the symptoms that sufferers of epididymitis can experience:
- Abnormalities in the scrotum, such as swelling, redness, and feeling warm
- Pain that usually occurs gradually in one testicle
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Frequent urination
- Pain when urinating
- Enlarged lymph nodes in groin
- Fever
When to see a doctor
Immediately do an examination to the doctor if you experience the above complaints, especially if the symptoms mentioned above do not subside after 4 days.
Immediate medical treatment in the emergency room should be carried out immediately in patients with severe pain in the testicles, pus coming out of the penis orifice, bloody sperm, and high fever.
Diagnosis of Epididymitis
To diagnose epididymitis, the doctor will ask questions and answers about the patient's symptoms and medical history. After that, the doctor will do a physical examination, including the penis and testicles.
If needed, the doctor can perform a digital rectal examination to detect disturbances in the prostate gland. Apart from that, there are several other examinations that doctors can do, namely:
- Blood and urine tests, to check for the presence of infection in the urinary tract
- Test a sample of fluid coming from the penis, to detect possible sexually transmitted diseases
- Doppler ultrasound, to check the smooth flow of blood in the testicles and detect testicular torsion
Epididymitis Treatment
Epididymitis treatment aims to treat the infection and relieve symptoms. Some of the treatment methods that can be done are:
Drugs
In epididymitis caused by a bacterial infection, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, doxycycline, or levofloxacin. These antibiotics need to be taken for 1–2 weeks. If the infection is a sexually transmitted infection, the patient's partner must also take antibiotics.
Generally, patients will improve within 2–3 days after taking antibiotics. However, it is important to remember that antibiotics must be taken until they run out even if the symptoms have subsided. After the antibiotics run out, check with the doctor to make sure that the infection is completely gone.
Apart from antibiotics, doctors can also prescribe pain and inflammation relievers, such as ibuprofen or paracetamol.
Operation
If a collection of pus (abscess) has formed in the epididymis, the doctor will perform surgery to remove the pus. In severe epididymitis, doctors can also perform surgical removal of the epididymis canal (epididymectomy).
Apart from dealing with the epididymis, surgery can also be performed to repair abnormal urinary tracts and trigger epididymitis.
Self care
To help heal the epididymis, patients are advised to make independent efforts at home, such as:
- Positioning the feet higher than the body when lying down so that the scrotum is lifted and not pressed
- Wearing pants that can support the scrotum
- Compress the scrotum with ice cubes wrapped in a clean towel or cloth
- Not lifting heavy weights
- Do not have sex until healed
Epididymitis complications
If left untreated, epididymitis can last in the long term (chronic) and cause the following complications:
- Collection of pus or abscess in the scrotum
- Death of tissue in the testicles (testicular infarction) due to obstruction of blood flow to the testicles
- Orchitis, which is inflammation of the testes that can spread from the epididymis
- Tearing of the scrotal skin layer
- Hypogonadism
- Fertility disorders
Prevention of Epididymitis
The way to prevent epididymitis is to avoid factors that can increase the risk of developing epididymitis, namely:
- Have healthy sex to avoid sexually transmitted infections
- Check with your doctor if you have a disease that is at risk of triggering epididymitis
- Get circumcised if you haven't already
Related Searches:
- epididymitis treatment,
- epididymitis symptoms,
- epididymitis causes,
- epididymitis treatments,
- epididymitis medication,
- chronic epididymitis,
- can you get epididymitis without having an std,
- epididymitis antibiotics,
- epididymitis recovery time,
- how i cured my chronic epididymitis,
- epididymitis icd 10,
- what causes epididymitis,
- my boyfriend has epididymitis,
- does ejaculating hurt epididymitis,
- epididymitis in women,
- epididymitis after vasectomy,
- acute epididymitis,
- epididymitis lump,
- what is epididymitis,
- symptoms of epididymitis,
- what is the best antibiotic to treat epididymitis,
- epididymitis doctor,
- causes of epididymitis,
- icd 10 code for epididymitis,
- orchitis and epididymitis,
- chronic epididymitis treatment,
- congestive epididymitis,
- testicular epididymitis,
- epididymitis infection,

Post a Comment for "Epididymitis, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications"