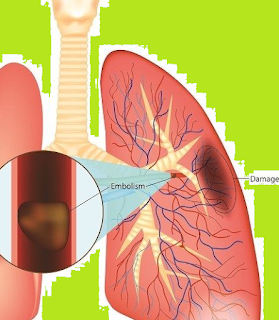
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in the blood vessels in the lungs. This blockage is usually caused by blood clots that initially form in other parts of the body, especially the legs. If not treated immediately, pulmonary embolism can endanger the life of the sufferer.
 |
| Pulmonary Embolism, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Complications |
In general, more than one blood clot forms and causes a pulmonary embolism. These blood clots will clog blood vessels and block blood flow to the tissues in the lungs, causing death in the lung tissue.
Causes of Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is most often caused by a blood clot from another part of the body that blocks a pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery itself is a blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the lungs.
In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by a blood clot that forms in deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT often occurs in the veins in the legs or pelvis.
In addition to blood clots, emboli in the pulmonary arteries can also be caused by other materials, such as:
- Air bubble
- Fat from broken bone marrow
- Part of the tumor
- A collection of bacteria, fungi, or parasites
- amniotic fluid
Pulmonary embolism risk factors
There are several factors that can increase a person's risk of developing a pulmonary embolism, namely:
- Have had a pulmonary embolism, DVT, cancer, stroke, or heart attack
- Have had chemotherapy or surgery, such as bone, joint, or brain surgery
- Unable to get out of bed, for example due to paralysis or long bed rest in hospital
- Suffer from a blood clotting disorder, overweight, obesity, or a broken bone, especially the femur or pelvis
- Have a family history of pulmonary embolism
- Are on hormone replacement therapy
- Are pregnant or have recently given birth
- Are taking birth control pills
- Have a smoking habit
- Over 40 years old
Pulmonary Embolism Symptoms
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism can vary, depending on the size of the affected part of the lung, the size of the blood clot, and the condition of the heart and lungs. Some of the symptoms and signs that generally appear as a result of a pulmonary embolism are:
- Shortness of breath that appears suddenly
- Chest pain that can radiate to the jaw, neck, shoulders and arms or chest pain that gets worse when you take a breath (pleuritic pain)
- Coughing up phlegm or blood
- Dizziness or fainting
- Pain that can be accompanied by swelling in the legs, especially the calves
- Fast and irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Fingertips or lips turning blue (cyanosis)
- Back pain
- Excessive sweating
When to see a doctor
Check with your doctor if you suddenly experience shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up phlegm accompanied by blood. These symptoms could be a sign of a pulmonary embolism and should be treated immediately.
Immediately see a doctor if you develop deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Blood clots in the legs due to DVT can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism if not treated quickly.
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism
The doctor will ask about the symptoms experienced by the patient, as well as a history of the disease the patient has had. After that, the doctor will do a physical examination, including checking for signs of DVT.
To determine whether the patient has a pulmonary embolism, the doctor will perform the following examinations:
- Blood test, to measure D dimer (a protein in the blood that appears after blood clots break down), as well as measure levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood
- Scan with duplex ultrasound, CT scan, ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan, or MRI, to detect the position of the blood clot in the body
- Pulmonary angiography, or pulmonary angiography, to see blood flow in the pulmonary arteries if other tests have not confirmed a pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
Pulmonary embolism treatment aims to prevent new blood clots from forming, as well as preventing blood clots that have already formed from growing. There are several methods for dealing with pulmonary embolism, namely:
- Administration of anticoagulant drugs, to inhibit the formation of blood clots, as well as thrombolytic drugs to break up blood clots
- Catheter installation, to prevent blood clots from entering the lungs
- Embolectomy surgery, to remove blood clots if they are too large and threaten the patient's life
Pulmonary Embolism Complications
Although dangerous, pulmonary embolism can be cured. However, if treated too late, patients with pulmonary embolism can experience complications in the form of:
- Fluid buildup in the lining of the lungs (pleural effusion)
- High blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs (pulmonary hypertension)
- Death of lung tissue (pulmonary infarction)
- Heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias)
- cardiac arrest
Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism
One way to prevent pulmonary embolism is to prevent DVT (deep vein thrombosis). There are several things that can be done, namely:
- Do regular physical activity every day.
- Move your arms and legs every few minutes if you're on a long journey.
- Wear compression stockings if you can't move much because of bed rest.
- Maintain body fluid levels by drinking lots of water, and limit consumption of caffeinated drinks.
- Lose weight until ideal if you suffer from obesity.
- Stop smoking.
In addition, if you suffer from a blood clotting disorder or are undergoing hormone replacement therapy, carry out regular controls to the doctor so that the condition is monitored.
Related Searches:
- pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism symptoms,
- symptoms of pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism treatment,
- what is a pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism icd 10,
- signs of pulmonary embolism,
- saddle pulmonary embolism,
- icd 10 code for pulmonary embolism,
- what is pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism treatments,
- pulmonary embolism causes,
- how long can you have a pulmonary embolism without knowing,
- life expectancy after pulmonary embolism,
- cause of pulmonary embolism,
- bilateral pulmonary embolism,
- how long before a pulmonary embolism kills you,
- icd 10 pulmonary embolism,
- how long can you have pulmonary embolism without knowing,
- pulmonary embolism medication,
- signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism diagnosis,
- pulmonary embolism ecg,
- what causes pulmonary embolism,
- signs and symptoms of a pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism sleeping position,
- stages of pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism x ray,
- pulmonary embolism xray,
- acute pulmonary embolism,
- signs of a pulmonary embolism,
- what is the first sign of pulmonary embolism,
- treatment for pulmonary embolism,
- what does pulmonary embolism feel like,
- what does a pulmonary embolism feel like,
- pulmonary embolism chest pain location,
- history of pulmonary embolism icd 10,
- symptoms of a pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism risk factors,
- pulmonary embolism signs and symptoms,
- causes of pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism test,
- test for pulmonary embolism,
- what causes a pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism survival rate by age,
- pulmonary embolism death,
- tests for pulmonary embolism,
- how to prevent pulmonary embolism,
- what are the warning signs of a pulmonary embolism,
- bilateral pulmonary embolism icd 10,
- testing for pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism pain,
- acute pulmonary embolism icd 10,
- pulmonary embolism tests,
- ct angiogram chest pulmonary embolism w contrast,
- d-dimer range for pulmonary embolism,
- icd 10 code for history of pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism back pain,
- pulmonary embolism survival rate,
- pulmonary embolism complications,
- pulmonary embolism covid,
- pulmonary embolism pregnancy,
- icd 10 for pulmonary embolism,
- ct scan pulmonary embolism,
- how to prevent a pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism doctor,
- chest x ray pulmonary embolism,
- complications of pulmonary embolism,
- how to diagnose a pulmonary embolism,
- christina desantis pulmonary embolism,
- icd 10 code pulmonary embolism,
- dvt pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism on chest x ray,
- ct chest pulmonary embolism protocol,
- pulmonary embolism chest x ray,
- how to diagnose pulmonary embolism,
- how to treat pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism nursing diagnosis,
- pulmonary embolism definition,
- pulmonary embolism prevention,
- icd 10 code for bilateral pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism diagnostic test,
- pulmonary embolism after surgery,
- icd 10 history of pulmonary embolism,
- what is a saddle pulmonary embolism,
- what are the symptoms of a pulmonary embolism,
- what is saddle pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism.,
- pulmonary embolism pain in back,
- diagnostic test for pulmonary embolism,
- symptoms pulmonary embolism,
- diagnostic tests for pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism postpartum,
- preventing pulmonary embolism,
- nursing diagnosis for pulmonary embolism,
- icd 10 code for acute pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism videos,
- pulmonary embolism mortality rate,
- prevention of pulmonary embolism,
- pulmonary embolism in spanish,


